Exploring Human Connection: The Fundamental Needs Charts in Montessori
In the Montessori elementary classroom, we support children’s natural curiosity about what it means to be human. One of the tools we use for this exploration is the Fundamental Needs Charts, which illustrate the universal needs that connect all people, past and present.
Understanding Our Shared Humanity
The purpose of these charts is to help children recognize their own needs and see how human beings across time and cultures have worked to fulfill them. Through this, children begin to develop a deeper awareness of their place in history and the common threads that unite all people.
There are two charts that children use first as an overview and then as a tool for research.
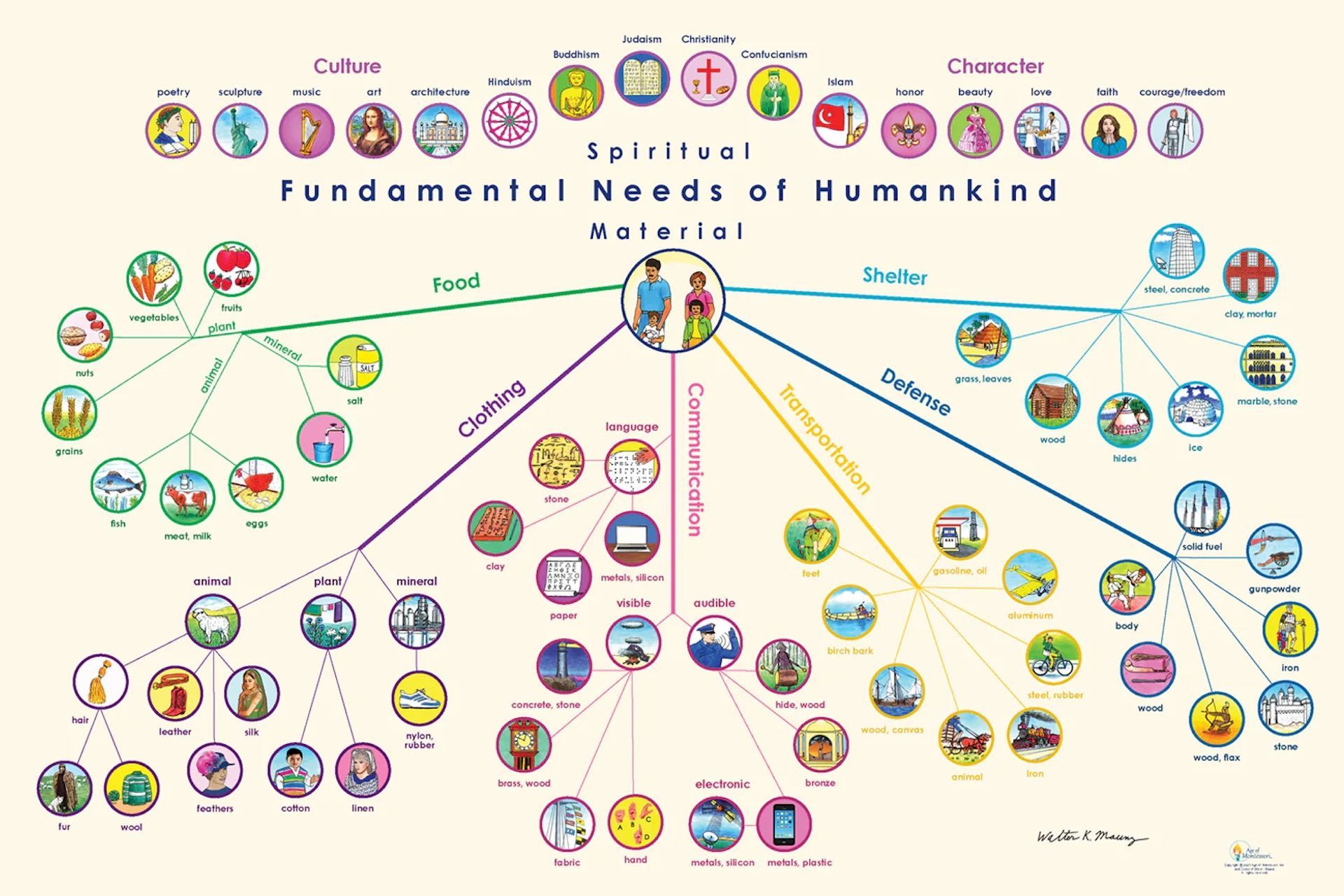
- The first chart provides a broad overview of fundamental needs, divided into material needs (food, shelter, clothing, defense, transportation) and spiritual needs (art, music, religion, communication).
- The second chart focuses specifically on the human need for food, a concept that even the youngest elementary students can appreciate!
Unlike traditional text-heavy resources, these charts rely on visual representations, which makes them accessible to younger elementary children. The charts also provide a visual model of how to organize an investigation into ancient civilizations and cultures.
A Framework for Exploration
Elementary-aged children are naturally curious about how things work and why people live the way they do. The Fundamental Needs Charts provide a structured way to study history and culture, allowing children to ask meaningful questions:
- How did different civilizations meet their needs for food and shelter?
- How did people create art, music, and systems of belief?
- What innovations, like the wheel, changed the way humans lived?
- Are spiritual needs as essential as physical ones for survival?
These questions encourage children to think critically and compare cultures in a way that fosters both curiosity and respect for diversity.
From Concrete to Abstract Thinking
At first, children relate to physical needs like food and warmth because they have personally experienced hunger or cold. They also begin to grasp more abstract concepts, such as the role of art, music, and communication in human development.
We introduce the first chart through conversation:
- What did you have for breakfast this morning?
- How did you get to school? Did you wear a seat belt?
- Why did you choose the clothes you have on today?
- What do you plan to do this weekend?
We often write little slips with students’ answers. Then, we display the first chart and, together with the children, figure out how to put the different answers into the different categories. Children love this personal connection to the material, and the process lays the stage for how information can be organized thematically.
Encouraging Independent Research
The Fundamental Needs Charts do not present every possible human need–this is intentional. Instead, they provide a model that encourages children to create their own charts based on their research. This process deepens their understanding and allows them to make connections between cultures in a meaningful way.
Younger children often love making “needs” collages from magazine pictures or even charts of their own personal “fundamental needs” such as “What I Eat.” Sometimes, children may make booklets or write a story or report about a particular aspect of the chart, such as “How We Get to School” or foods that come from fish or foods that are flowers! Or they may make a chart with all the different ways human beings transport themselves, or about human houses. The possibilities are endless!
As they continue their studies, older children transition to The History Question Charts, which rely more on text and research. These allow for a more detailed examination of historical patterns, further reinforcing the idea that history is a story of human beings working to meet their needs.
Education for Peace
Dr. Maria Montessori believed that education should help children see themselves as part of a larger human family. By studying the universal needs that all people share, children develop a sense of human solidarity through space and time. They learn that while cultures may differ in their approaches, our fundamental needs unite us all.
This understanding fosters empathy, respect, and a sense of interconnectedness—essential components of education for peace. The Fundamental Needs of Human Beings Charts are more than just learning tools; they are a gateway to understanding human history, culture, and identity.
Visit our classrooms to see how our learning activities help young people become interconnected citizens!





